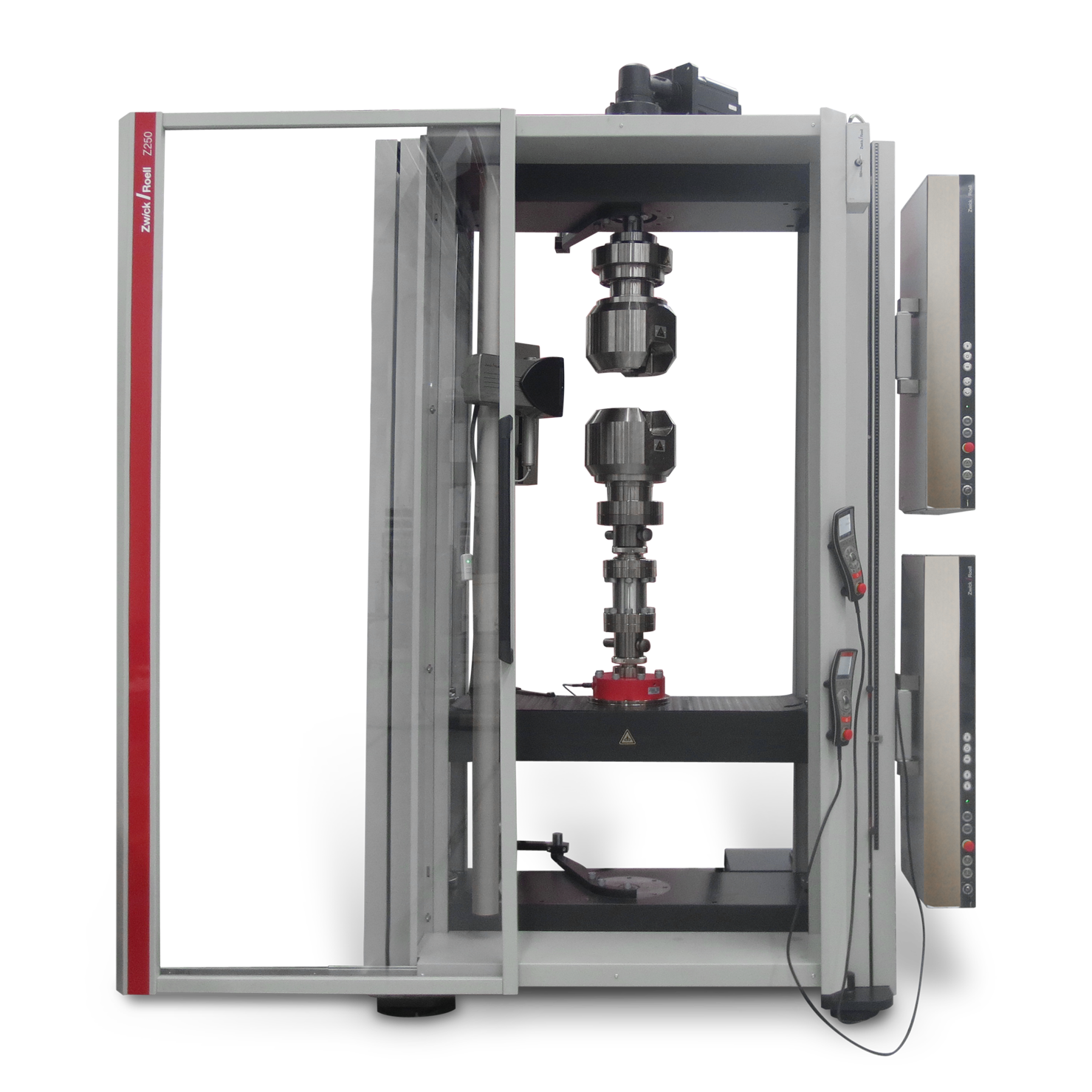
Torsion testers
Download- Plastics
- Metals
- Automotive
- Medical
- 2.5 - 250 kN
- 2 - 2,000 Nm
- Uniaxial or biaxial torsion test
What is torsion testing?
The torsion test is a mechanical test method used to examine the deformation of a specimen through a twisting/rotating motion.
Torsion, in its simplest form, is the action of twisting. Many everyday materials, components, component assemblies, and end-user products used in various industries are designed with the primary purpose of supporting this direction of movement. Products include screws, springs, syringe components, wire, tubing, and many more.
In the world of materials testing, we use torsion testers to simulate this twisting motion and help manufacturers determine important material properties, including:
- Maximum torque
The maximum torque (twisting force) value that can be applied before specimen failure. Once the maximum torque is found on a screw or bolt, for example, a safety factor can be calculated and built into the torque strength specifications of that product. - Torsional strength
The ultimate strength of a specimen, and the maximum torsional stress that a specimen that is subjected to a torsional load can withstand before failure. - Torsional shear stress
Shear stress that acts on a transverse cross section of the specimen due to torsional motion. Torsional loading creates uneven stress distribution over the cross section of the specimen, ranging from zero in the center to maximum torsional shear stress at the edge of the specimen. - Modulus of elasticity in shear
Elastic shear stiffness defined as the ratio of shear stress to shear strain. When comparing identical products, the higher the modulus of elasticity of the material, the greater the stiffness. The greater the stiffness or rigidity of a structure, the more force is required to cause deformation. - Breaking angle of the specimen
The breaking angle provides a measure of the ductility of a material when undergoing a torsional moment. According to ASTM F543-13, for example, a medical bone screw with a greater breaking angle may provide an earlier tactile warning to the surgeon that it is reaching its maximum torsional strength.
Depending on your torsion test application, torsion testing machines can be set up to run on material specimens up to the point of failure or based on a defined torque and duration. They can also be run on finished product assemblies, such as pharmaceutical pen injectors or screw caps to determine proper function of the device.
Torsion testing machine applications
ZwickRoell torsion testing equipment
Our torsion testing machines and torsion drives cover a wide range of torsion tests and can be adapted to your specific applications.
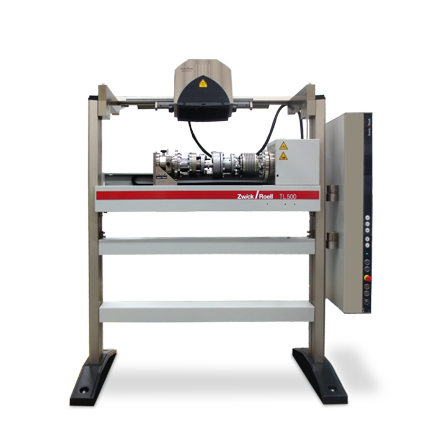
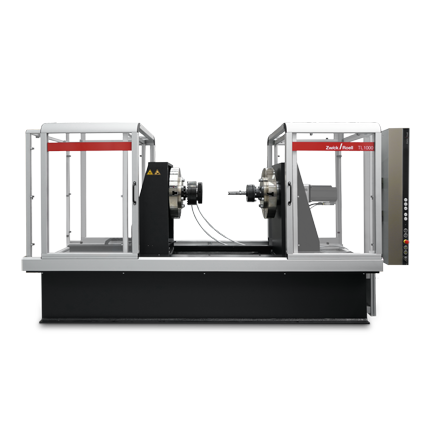
- TorsionLine
Torsion testing machine with horizontal torsion axis, maintenance-free AC servo drive and torque range from 20 Nm to 500 Nm or 1,000 Nm to 2,000 Nm for single-axis torsion tests. - zwickiLine
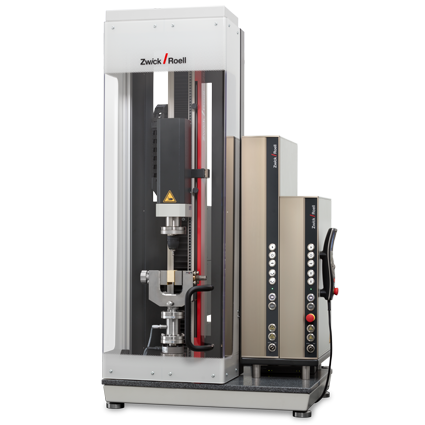
Equipped with either a 2 Nm or 20 Nm torsion drive for test loads up to 5 kN for axial tests and axial torsion tests (tensile or compression combined with torsion) - AllroundLine
Table-top or floor-standing machine equipped with a 200 Nm or 2,000 Nm torsion drive for test loads up to 250 kN for axial tests and axial torsion testing (tensile or compression combined with torsion) - Torsion drives
Modular torsion drives with torques from 2 Nm to 2,000 Nm for easy retrofitting of your existing zwickiLine or AllroundLine materials testing machine.
testXpert testing software
ZwickRoell torsion test machines for axial tests and axial torsion tests seamlessly interact with our test tools and accessories, our testXpert testing software and our testControl measurement and control electronics.
testXpert III features a standard-compliant master test program, pre-configured for multiple test axes and includes our graphical sequence editor for freely programmable test sequences using simple function blocks.
How do torsion testers work?
Materials testing machines are equipped with a torsion drive, which operates and controls the torque and speed of the rotating motion. Depending on your testing needs, you can use these torsion tests to perform uniaxial and multi-axis load tests (tensile or compression combined with torsion) .
To run a test, your specimen is placed in the grips of the torsion testing machine and one end of the specimen is twisted around the long axis for a specified number of turns, a specified amount of time, or until failure, depending on your application and test purpose.
The torque or twisting force applied to the specimen induces torsion on the specimen, causing a distribution of stress over the specimen’s cross-sectional area (shear stress). This differs from tensile or compressive loads, which produce uniform stress over the specimen’s cross section.
Common standards for torsion testing
- ASTM A938-18 – Standard Test Method for Torsion Testing of Wire
Wire is twisted at a defined speed and the number of total turns to fracture is determined. If the number of turns is satisfactory, the specimen is considered to have passed the test. - ASTM F543-13 – Standard Specification and Test Methods for Metallic Medical Bone Screws
This standard applies to metallic bone screws that are implanted into bone. The torsional strength is tested to ensure that the screw does not break during insertion or removal. Properties measured include the torsional yield strength, maximum torque, and the breaking angle under standard conditions. - ISO 7800 – Metallic materials – Wire – Simple torsion test
Used to determine the ability of metallic wire with a diameter or characteristic dimension from 0.1 mm to 14 mm to undergo plastic deformation during simple torsion in one direction. The test is run until the specimen breaks or until a specified number of turns is reached. - ISO 7206-8 – Implants for surgery – Partial and total hip joint prostheses – Part 8:Endurance performance of stemmed femoral components with application of torsion
Femoral components are tested in their ready-for-use condition and may not fracture during the specified number of cycles and test load, as specified by the standard.
Technical overview
| TorsionLine 20/200/500 | TorsionLine 1000/2000 | zwickiLine | AllroundLine | AllroundLine | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
 |  |  |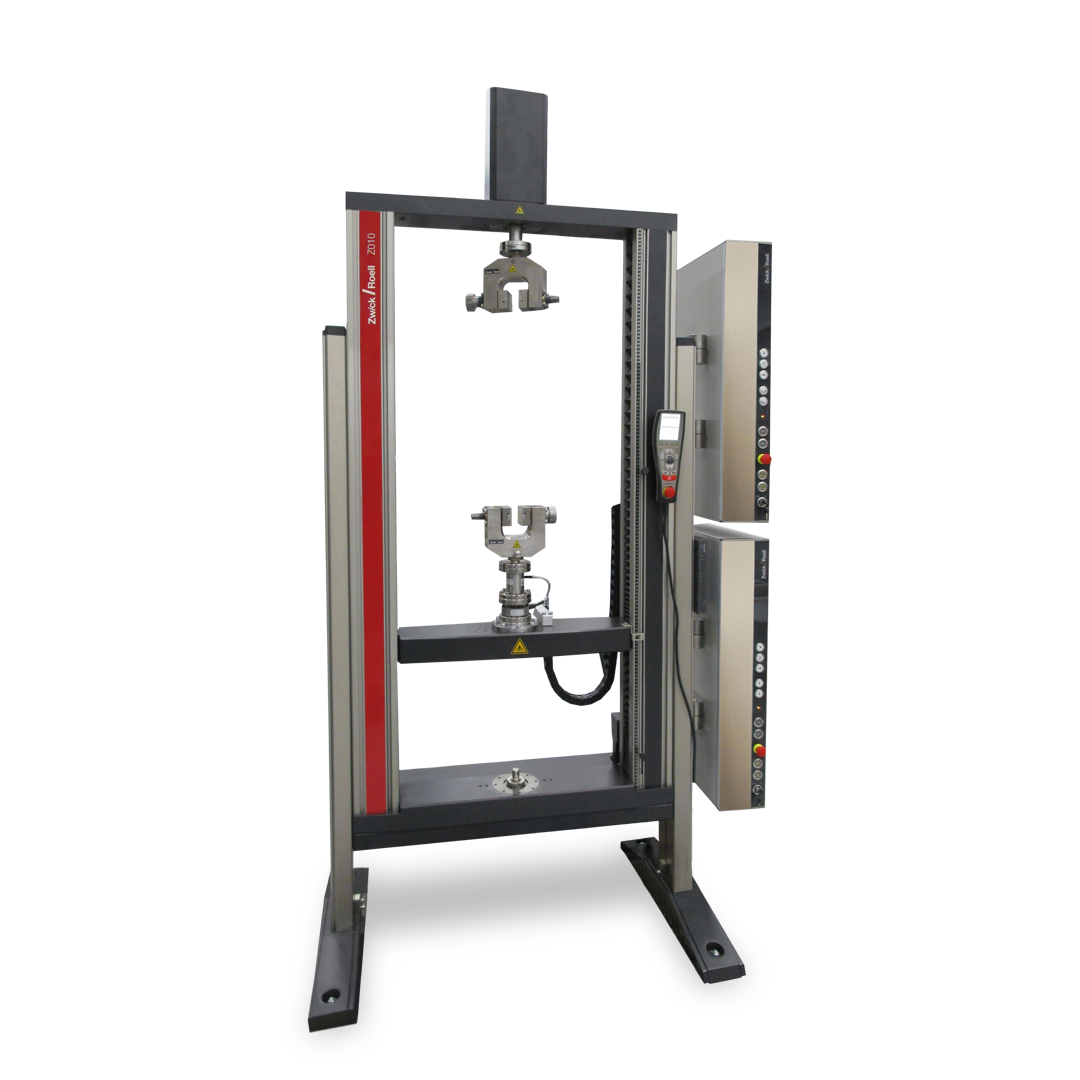  | 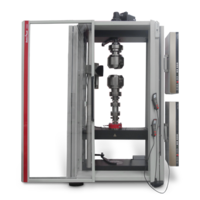 | |
| Model | Floor-standing testing machine | Floor-standing testing machine | Table-top testing machine | Table-top testing machine | Floor-standing testing machine |
| Type of test | Torsion Test | Torsion Test | Tensile-compression-torsion | Tensile-compression-torsion | Tensile-compression-torsion |
| Test axis | Horizontal | Horizontal | Vertical | Vertical | Vertical |
| Max. axial force | - | - | 2.5 kN 5 kN | 50 kN | 250 kN |
| Torsion drive | 20 Nm 200 Nm 500 Nm | 1,000 Nm 2,000 Nm | 2 Nm 20 Nm | 2 Nm 20 Nm 100 Nm 200 Nm | 200 Nm 2000 Nm |
| Torsion drive can be retrofitted | - | - | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ |
| Typical applications |
|
|
|
|
|
| Item No. | 1020233 | 1023835 | |
| Nominal torque Mnom | 2 | 20 | Nm |
| Permissible axial force | 2.5 | 5 | kN |
| Drive | |||
| Rotational speeds | 0.01 ... 801 0.01 ... 202 | 0.01 ... 801 0.01 ... 202 | rpm |
| Pitch circle connection flange Ø | 40/753 | 40/753 | mm |
| Power consumption | 0.5 | 0.8 | kVA |
| Electrical power specifications | 230 V AC, 50/60 Hz, 1Ph/PE/N | 230 V AC, 50/60 Hz, 1Ph/PE/N | |
- Maximum speed. Only in conjunction with a safety device
- Reduced speed when operating without a safety device
- Additional adapter flange with mounting stud Ø 20 mm included in the scope of delivery.
| Item No. | 1020233 | 1023835 | 1027734 | 1027737 | 3005980 | |
| Nominal torque Mnom | 2 | 20 | 100 | 200 | 200 | Nm |
| Permissible axial force | 2.5 | 5 | 5 | 50 | 50 | kN |
| Drive | ||||||
| Rotational speeds | 0.01 ... 801 0.01 ... 202 | 0.01 ... 801 0.01 ... 202 | 0.002 ... 601 0.002 ... 202 | 0.002 ... 20 | 0.005 ... 501 0.005 ... 202 | rpm |
| Pitch circle connection flange Ø | 40/753 | 40/753 | 75 | 75/115 | 75/115 | mm |
| Electrical power specifications | 230 V AC, 50/60 Hz, 1Ph/PE/N | 230 V AC, 50/60 Hz, 1Ph/PE/N | 230 V AC, 50/60 Hz, 1Ph/PE/N | 230 V AC, 50/60 Hz, 1Ph/PE/N | 400 V AC, 50/60 Hz, 3Ph/PE/N | |
| Power consumption | 0.5 | 0.8 | 2.3 | 2.3 | 5 | kVA |
- Maximum speed. Only in conjunction with a safety device
- Reduced speed when operating without a safety device
- Additional adapter flange with mounting stud Ø 20 mm included in the scope of delivery.
| Item No. | 1024998 | 1025005 | |
| Nominal torque Mnom | 200 | 2000 | Nm |
| Permissible axial force | 250 | 250 | kN |
| Drive | |||
| Rotational speeds | 0.001 ... 10 | 0.002 ... 10 | rpm |
| Pitch circle connection flange Ø | 115/2201 | 115/2201 | mm |
| Electrical power specifications | 230 V AC, 50/60 Hz, 1Ph/PE/N | 400 V AC, 50/60 Hz, 3Ph/PE/N | V |
| Power consumption | 2.2 | 5 | kVA |
- Additional adapter flange with locking pin connection included in the scope of delivery
| Type | TL 020 | TL 200 | TL 500 | |
| Item No. | 1026875 | 1026878 | 1026879 | |
| Load frame | ||||
| Torque (left/right) | 20 | 200 | 500 | Nm |
| Total height with safety device | 1775 | 1775 | 1775 | mm |
| Total width with safety cover | 1475 | 1475 | 1475 | mm |
| Total depth | 650 | 650 | 650 | mm |
| Height of test axis | Adjustable | Adjustable | Adjustable | |
| Safety device | Electrically interlocked | Electrically interlocked | Electrically interlocked | |
| Anti-rotation device of torque transducer | Manually operated, electrically monitored | Manually operated, electrically monitored | Manually operated, electrically monitored | |
| Weight with electronics, safety cover, torque transducer | 185 | 188 | 188 | kg |
| Grip to grip separation with 4-jaw chuck, max. | 510 | 510 | 510 | mm |
| Grip-to-grip separation with universal flanges (without specimen grip), max. | 680 | 680 | 680 | mm |
| Diameter of specimens/specimen holders, max. | 200 | 200 | 200 | mm |
| Finish | RAL 7011 and RAL 7038 | RAL 7011 and RAL 7038 | RAL 7011 and RAL 7038 | |
| Ambient temperature | +10 ... +35 | +10 ... +35 | +10 ... +35 | °C |
| Relative humidity (non-condensing) | 20 ... 90 | 20 ... 90 | 20 ... 90 | % |
| Noise level | 70 | 70 | 70 | dB(A) |
| Torsion inherent stiffness | > 1000 | > 1000 | > 1000 | Nm/° |
| Axial frictional force when driving the carriage (without torsion load), approx. | 4 | 4 | 4 | N |
| Drive | ||||
| Rotational speed | ||||
| In turns | 0.0005 ... 180 | 0.0005 ... 90 | 0.0005 ... 50 | rpm |
| In degrees | 0.072 ... 64800 | 0.036 ... 32400 | 0.036 ... 18000 | °/min |
| Angle resolution of the drive | 3.29 | 1.89 | 0.92 | Rotational second/minute |
| Positioning repeatability (without reversing directions) | ||||
| At 1000 °/min | ≤20 | ≤10 | ≤10 | Rotational seconds |
| Play at zero torque crossing | < 1 | < 1 | < 1 | Rotational minutes |
| Power specifications | ||||
| Electrical connection | 230V, 1 Ph/N/PE | 400V, 3 Ph/N/PE | 400V, 3 Ph/N/PE | |
| Power consumption | 2.2 | 7 | 7 | kVA |
| Frequency | 50/60 | 50/60 | 50/60 | Hz |
| Type | TL 1000 | TL 2000 | |
| Item No. | 1026880 | 1026881 | |
| Load frame | |||
| Torque (left/right) | 1,000 | 2000 | Nm |
| Total height with safety device | 1450 | 1650 | mm |
| Total width with safety cover | 2358 | 2580 | mm |
| Total depth | 860 | 843 | mm |
| Height of test axis, from the floor | 935 | 958 | mm |
| Safety device | Electrically interlocked | Electrically interlocked | |
| Weight with electronics, safety cover, torque transducer | 1500 | 1400 | kg |
| Grip-to-grip separation with face-plate, without specimen holder, max. | 1,000 | 1,000 | mm |
| Diameter of specimens/specimen holders, max. | 600 | 600 | mm |
| Finish | RAL 7011 and RAL 7038 | RAL 7011 and RAL 7038 | |
| Ambient temperature | +10 ... +35 | +10 ... +35 | °C |
| Relative humidity (non-condensing) | 20 ... 90 | 20 ... 90 | % |
| Noise level | 62 | 62 | dB(A) |
| Torsion inherent stiffness | > 11,500 | > 11,500 | Nm/° |
| Specimen holders | |||
| Connection to load frame (gearing, torque transducer) via the face plate: | |||
| Diameter of specimen mounting flange, drive system | 400 | 400 | mm |
| Drive | |||
| Rotational speed | |||
| In turns | 0.0005 ... 20 | 0.0005 ... 10 | rpm |
| In degrees | 0.18 ... 7200 | 0.18 ... 3600 | °/min |
| Angle resolution of the drive | 0.5 | 0.2397 | Rotational second/minute |
| Positioning repeatability (without reversing directions) | |||
| At 1000 °/min | ≤5 | ≤5 | Rotational seconds |
| Play at zero torque crossing | < 5 | < 5 | Rotational minutes |
| Power specifications | |||
| Electrical connection | 400 | 400 | V, 3 Ph/N/PE |
| Power consumption | 5 | 5 | kVA |
| Frequency | 50/60 | 50/60 | Hz |
Downloads
- Product Information: zwickiLine for Torsion Testing PDF 226 KB
- Product Information: Tabletop Testing Machine for Torsion Testing PDF 449 KB
- Product Information: Floor-Standing Testing Machine for Torsion Testing PDF 248 KB
- Product Information: TorsionLine 20 to 500 Nm PDF 263 KB
- Product Information: TorsionLine 1000 to 2000 Nm PDF 338 KB
Frequently asked questions about torsion testing machines
The torsion test is a mechanical test method in which a specimen is twisted.
Torsion testing is used to simulate a twisting motion and help material manufacturers determine important characteristic values. These include maximum torque (twisting force), torsional strength (break resistance under torsional load), torsional shear stress, elastic shear stiffness (modulus of elasticity in shear), as well as the breaking angle of the specimen (ductility).
Torsion testing machines are used to simulate the torsional movement of materials, components or end-user products. The torsion drive of the materials testing machine operates and controls the torque and speed of the rotating motion. To run a test, the specimen is placed in the grip of the torsion testing machine. Depending on the application and test purpose, one end of the specimen is twisted around the long axis for a specified number of turns, a specified amount of time or until failure.
In the world of materials testing, we use torsion testers to simulate a twisting motion and help manufacturers determine important properties of every day materials, components and end user products. Torsion tests are used on many different applications and range from tests on bone screws, Luer lock connections, pen injectors, and screw caps in the medical and pharmaceutical industry to torsion loads on camshafts and torsion tests on metallic materials such as connectors, screws, wires, and much more.





