ASTM D6641 Combined Loading Compression
ASTM D6641 is a standard test method for determining the Young’s modulus, strength and strain at break of fiber composite laminates under compressive load. The test is suitable for 0°, 90° or multidirectional UD laminates, for woven and laid scrim composites or for fiber composites with discontinuous and randomly distributed reinforcing fibers (e.g. chopped fiber composites, SMC).
In the combined loading compression test, a combined force is applied by a normal force component via the end faces and by a shear force component via the clamped part of the specimen. This combined force application is particularly advantageous for compression tests on fiber composite laminates with high strengths. Compliance with the tolerances specified in the standard for the parallelism of the specimen end faces and for the perpendicularity of the end faces to the direction of loading is essential to achieve optimum results.
In accordance with ASTM D6641, both untabbed specimens (Procedure A) and tabbed specimens (Procedure B) can be used. See section "Test specimens and dimensions" below for more information.
Other frequently used test standards for compression tests on long or continuous fiber-reinforced plastics are ASTM D695 or DIN EN 2850 method B according to the pure end loading principle and ASTM D3410 or ISO 14126 method 1 according to the pure shear loading principle. Another standardized combined loading compression test is described in ISO 14126 method 2.
Objective and characteristic values Running a test CLC test fixture Testing machines Strain measurement Test requirements Specimen
Objective of the test and determined characteristic values to ASTM D6641
Compression tests for composites according to ASTM D6641 are carried out to determine the mechanical compression properties during material development and qualification, to determine characteristic values for the layout and design of composite structures and in quality assurance.
The combined loading compression test according to ASTM D6641 can be used to determine the following characteristic results and values:
- Compressive stress: compressive force related to the initial cross section of the specimen
- Compressive strain: change in gauge length with reference to the initial gauge length in load direction
- Compressive modulus: slope of the stress-compression curve in the compression test in a defined strain interval in the elastic range. Also called modulus of elasticity or Young’s modulus
- Compressive strength: maximum compressive stress carried by a specimen during a compression test
- Strain at break: compression when compressive strength is reached
If a biaxial strain gauge is used, with which the strain in the longitudinal and transverse direction can be measured, the Poisson's ratio could also be determined in the compression test according to ASTM D6641 and is discussed accordingly in the standard. However, this is impractical due to the relatively small free specimen length in the compression test and is therefore very rarely practiced. The tensile test according to ISO 527-4,-5 or ASTM D3039 is much more suitable for determining the Poisson's ratio.
How is the compression test according to ASTM D6641 carried out?
Below you will find important information on carrying out the combined loading compression test on composites and the required testing machines, testing devices and strain gauges. For detailed information on ASTM D6641, it is essential to purchase the standard.
ASTM D6641 combined loading compression test fixture
For the combined loading compression (CLC) test to ASTM D6641, a test fixture is required that enables the combined application of force via the end faces and via the gripped part of the specimen.
In the combined loading compression fixture shown in the standard, the specimen is gripped via 4 bolts each in the upper and lower, mutually guided part of the fixture. The end faces of the specimen are flush with the end faces of the device. The test fixture with the installed specimen is then placed between parallel aligned hardened compression platens and loaded under pressure until the specimen breaks.
In accordance with ASTM D6641, a comparable test fixture can also be used for the combined loading compression test that corresponds to the principle of combined force application in the test specimen:
The hydraulic composites compression fixture (HCCF), available exclusively from ZwickRoell for compression tests on composites up to 250 kN, is an extremely versatile compression fixture that is also suitable for the combined loading compression test to ASTM D6641.
Some advantages and features of the HCCF
- Enables compression tests to be carried out according to the combined loading compression principle (ASTM D6641, ISO 14126 method 2 or Airbus AITM 1-0008)
- Enables compression tests to be carried out according to the pure shear loading principle (ASTM D3410 or ISO 14126 method 1)
- For compression forces up to 250 kN
- For specimen widths up to 35 mm and laminate thicknesses up to 10 mm
- Fast specimen throughput during the test, as the HCCF remains in the testing machine
- Jaws are precisely aligned with each other and no displacement of the jaws in relation to each other during the test
- Unrestricted view of the free part of the specimen enables the use of optical strain measurement methods such as digital image correlation (DIC)
Note: ASTM D6641 requires double-sided strain measurement on the opposite surfaces in the free part of the specimen. Due to the relatively small area of 13x13 mm² of the standard ASTM D6641 specimen geometry, strain gauges are generally the most suitable method for strain measurement.See the “ Strain measurement ” section below for more information.
- A deformation caused by deviations in the adhesive layer or thickness of the tabs when clamping the specimen—recognizable by an absolute difference of >150 µe between the strain gauges measuring on both sides—can be corrected quickly and easily by opening the jaws and shimming.
- Can be used for compression tests in a temperature range of -60 °C to +150 °C
- Manually operated hydraulic pumps enable very precise specimen clamping
Jaw inserts with a scale pattern or with a rough surface applied using a thermal coating process are available for the HCCF. The jaws with thermal coating should be used when testing untabbed specimens (ASTM D6641 procedure A).
Testing machine for ASTM D6641
For compression tests to ASTM D6641 with standard specimens and for many other standardized test methods for fiber-reinforced plastics, use of a 100 kN AllroundLine testing machine is often sufficient. Shown is the test setup for compression tests with an HCCF compression fixture and extension rods at the top and bottom, which enables the performance of compressions tests in the temperature chamber. The extension rods are not required for compression tests at room temperature. With the 100 kN machine configuration shown, the use of mechanical body-over-wedge specimen grips for tensile tests (see small image at the top right) makes it easy to switch between different test setups and test fixtures. By simply removing the specimen grips, the entire working area of the testing machine can also be used for non-standard tests. The support legs enable individual and ergonomic adjustment of the work area height.
If testing is performed exclusively on glass fiber-reinforced plastics (GFRP), a static machine with a maximum force of 50 kN is normally sufficient.
Modular testing system for composites
Larger testing laboratories with correspondingly high test volume use different testing machines for the very diverse composite testing methods, and can thereby minimize conversion efforts. The individual testing machines can be adjusted to the force range required for the various types of tests. If throughput rates are not high or consistent enough that an investment in multiple testing machines makes sense, an alternative option is to equip a single testing machine so that you can perform as many test methods as possible with the least amount of machine conversion effort.
ZwickRoell developed a modular design, which is available as a 100 kN or 250 kN testing machine covering 21 test methods and approximately 120 test standards (ISO, EN, ASTM, as well as Airbus AITM and Boeing BSS), and which allows for comprehensive characterization of fiber-reinforced composite materials at ambient temperature or for tests at low or high temperatures ranging from -80 °C to +360 °C.

Reliable testing to ASTM D6641 thanks to our testXpert testing software
Our testXpert testing software supports efficient testing and reliable test results in accordance with ASTM D6641:
- Eliminate the need to study the standards: Guaranteed compliance with standards through standard test programs—all characteristic values and parameters of ASTM D6641 are already stored.
- You can achieve maximum testing efficiency by connecting peripheral devices: Sending the specimen dimensions from the micrometer or caliper directly to the testing software saves time and eliminates input errors.
- Check and control the temperature in the chamber via the software as well. Set temperature ramps and see the values that have been maintained retrospectively, with traceability.
Strain measurement using a compression test in accordance with ASTM D6641
The compression test according to ASTM D6641 requires double-sided and independent strain measurement in the free unsupported area of the specimen (gauge length). Due to the relatively small area of 13x13 mm2 of the nominal specimen geometry, the use of strain gauges applied on both sides is the most suitable method of strain measurement.
Double-sided and independent strain measurement on the specimen is required to detect any percent bending and to distinguish valid from invalid tests. See section Test conditions – Monitoring of superimposed bending deformation (percent bending) below.
Due to the open design of the HCCF compression fixture, it is also possible to use a clip-on extensometer that measures independently on both sides. However, a free length of at least 13 mm is required for this. A longer free length is permissible according to ASTM D6641 and is advantageous for the use of a clip-on extensometer, provided that the specimen thickness is dimensioned accordingly to avoid Euler buckling.
Test conditions according to ASTM D6641
Test speed
The nominal test speed according to ASTM D6641 is 1.3 mm/min.
Valid specimen failure
ASTM D6641 provides a 3-letter code for the documentation of specimen failure, which clearly defines the failure mode and the position along the specimen. Depending on the fiber architecture and the tested laminate, different valid failure modes can occur in the compression test, e.g. fracture across the specimen width, angled shear fracture through the specimen thickness (usually in compression tests on 90° UD laminates), kink band, brooming, splitting, delamination or combinations of different valid failure modes.
The compression test is only valid if the specimen breaks within the free length. A fracture in the middle area of the free length corresponds to the ideal case, but due to the short free length and the partially angled fracture surfaces, fractures also occur at the transition from the jaws to the free area or at the transition from the tab to the free area. This is also considered a valid specimen failure.
Invalid failure types are Euler buckling or failure at the specimen end faces as well as any type of specimen failure in the clamping area.
Monitoring of percent bending
In addition to valid specimen failure, for an overall valid compression test in accordance with ASTM D6641, percent bending on the compressive load shall not exceed a specified range. The percent bending value calculated for this is determined using the strain signals ε1 and ε2 determined on both sides of the test specimen using the formula By=(ε1-ε2)/(ε1+ε2)×100.
For a valid test: By<10% in the mean elongation interval of the Young’s modulus determination at 2000 µε and By<10% for compressive strength and strain at break.
If jumps and discontinuities occur in the strain signal due to pre-failure in the laminate near the breaking strength, the test is valid even if the percent bending criterion is met at 90% of the compressive strength.
Temperature range
Since the mechanical properties of fiber-reinforced plastics can be largely temperature dependent, in addition to compression tests at ambient temperature, tests are also performed at low and elevated temperatures. For this purpose, the ZwickRoell HCCF compression fixture can be used in a temperature range from -60° to +150 °C, which covers common spans of temperature tests between -40° and +80 °C (+120 °C) for automotive applications and between -55 °C and +120 °C in aviation.
ASTM D6641 specimens and dimensions
| Specimen type | Schematic representation of the specimen | Notes |
|---|---|---|
| Untabbed (Procedure A) | 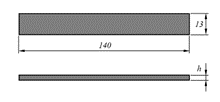 | Can be used for multidirectional laminates with less than 50% 0° plies if failure at the end faces of the specimen can be avoided and does not require a large increase in gripping force above the recommended level. |
| Tabbed (Procedure B) | 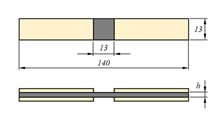 |
|
- A ±45° GRP laminate can be used as the tab material, which is glued to the laminate to be tested using a suitable adhesive. For specimen thicknesses up to 2.5 mm, a tab thickness of approx. 1.6 mm has proven to be suitable. For thicker specimen thicknesses, thicker tabs should be selected if necessary.
- ASTM D6641 does not define a standard specimen thickness. Specimen thicknesses of 2 to 3 mm are usually tested. Thicker laminates can also be tested, provided that the compression test fixture used for this purpose is suitable. For smaller specimen thicknesses, the dimensioning against Euler buckling specified in the standard must be observed, especially for laminates with low stiffness
- The HCCF compression fixture was originally developed for the combined loading compression test according to Airbus AITM 1-0008. The length of the jaws specified in AITM 1-0008 is 65 mm. The original jaws of the HCCF are therefore 1.5 mm too long for the standard ASTM D6641 specimen geometry. 143 mm long compression specimens must be used to perform the combined loading compression test according to ASTM D6641 with the HCCF. Alternatively, suitable jaws designed for the nominal specimen length of 140 mm can be used.