GIc Test / DCB Test According to ASTM D5528 and ISO 15024
The G1c test according to ASTM D5528 or ISO 15024 can be used to determine the critical interlaminar energy release rate of composite laminates for crack initiation and crack propagation in the laminate under mode I loading. Due to the specimen geometry used, the test is often referred to as the DCB (double cantilever beam) test.
Due to the importance of this test method and this material property for the layout and design of composite structures in the aerospace sector, there are also special industry standards at Airbus (AITM 1-0005) and Boeing (BSS 7273). These, however, when compared to ASTM D5528 and ISO 15024, use a different procedure referred to as the area method for the calculation of results.
Objective & applications DCB specimen Running a test Video Test equipment Downloads Request a consultation
Objective and applications of the GIc test
Delamination in fiber composites refers to the detachment or non-connected individual layers within a laminate. Such damage or defects reduce the mechanical properties of the laminate and are therefore particularly critical for composite structures.
Under unfavorable loading and when the critical value of the interlaminar energy release rate of the present composite material is reached, crack propagation occurs in the laminate. If this occurs through a tensile force perpendicular to the crack plane, it is referred to as mode I loading.
By using the DCB test (double cantilever beam) according to ASTM D5528 or ISO 15024, initiation and propagation values of the critical interlaminar energy release rate under mode I load can be reliably determined.
Double cantilever beam (DCB) specimen
The double cantilever beam (DCB) specimen according to ASTM D5528 and ISO 15024 is made from a composite specimen plate with a thin separating film inserted on one side in the symmetry plane of the laminate. The specimens taken from this can then be bent open like bending beams on the side with the laminated crack (hence the name double cantilever beam), while the individual layers of the composite are still connected in the remaining part of the specimen.
Load application blocks or hinged tabs are usually bonded to the specimen for load application. Markings are applied to the specimen edge in accordance with the relevant standard specifications to visually monitor the progress of the crack during the test.
Running a test according to ASTM D5528 & ISO 15024
The force application elements of the DCB specimen (loading blocks or hinged lugs) are connected to the specimen grips of the testing machine. Since the fabricated crack at the end of the laminated release film is often not sharp enough and therefore an unrepresentative G1c value can be determined, the crack is first widened slightly and a sharp pre-crack is produced. The length of the pre-crack is precisely determined, and then the load is fully removed from the specimen. In the second part of the DCB test, the specimen is loaded again until the crack has reached the end of the laterally applied markings.
Three different criteria are described in ISO 15024 for the initiation value of the critical energy release rate (applies for pre-crack and for full crack propagation):
- Onset of non-linearity (NL): With pure elastic deformation of the specimen halves, the force-displacement curve in the test is initially linear. The force-displacement value pair at which the non-linearity of the force-displacement curve begins is used to calculate the initiation value.
- Visible crack propagation (VIS): The force-displacement value pair of the force-displacement curve, at which the crack propagation visibly begins, is used to calculate the initiation value.
- Compliance criterion (5% or max): For this criterion, the force-displacement value pair is determined at which the compliance of the originally linear part of the force-displacement curve is reduced by 5%. If the maximum force is reached beforehand, this force-displacement value pair is used.
The initial crack length is used for the respective initiation value (from laminated crack or from pre-crack). In the current edition of ASTM D5528, only the compliance criterion is used to determine the initiation value of the critical energy release rate.
Propagation values are determined for crack lengths and corresponding force-displacement value pairs on the markings applied to the sides. The crack growth is monitored visually on the side of the specimen. It is very important that the recording of force, displacement and crack length is synchronized.
The crack length can be evaluated manually by an operator who follows the crack progress with a magnifying glass or computer-controlled with a video recording system.
Different evaluation methods are used in the two standards to calculate the R-curve (critical energy release rate plotted against crack length, includes initiation and propagation values):
- ISO 15024 contains calculations according to the corrected beam theory (CBT) and according to the modified compliance calibration (MCC) method.
- ASTM D5528 uses the compliance calibration (CC) method and lists other methods in the appendix. The reduction to the CC method was made here to ensure comparability between the G2c fracture toughness values determined according to ASTM D7905 under mode II loading.
Test equipment for the GIc test to ASTM D5528 and ISO 15024
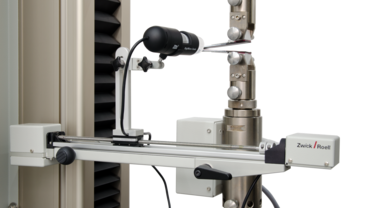
The ZwickRoell single-column table-top testing machine is particularly suitable for the GIc test to ASTM D5528 and ISO 15024.
By using the motorized video recording system for G1c tests, crack propagation measurements become traceable and more convenient. A digital camera is used to record the progress of the crack along the specimen and create a video of the entire test. Using the video created, each individual test can be checked retrospectively in case of doubt and the measured values can be corrected as the crack progresses.
The testXpert testing software greatly simplifies the execution and evaluation of the G1c test. On the one hand, the camera is connected to testXpert so that the crack progress can be conveniently tracked on the screen. On the other hand, testXpert has preconfigured standard programs that contain all the methods for calculating the initiation and propagation values of the critical interlaminar energy release rate in accordance with the specifications in ASTM D5528 or ISO 15024.