Calculation of the N-Value to ISO 10275 and ASTM E646
The determination of the hardening exponents to ISO 10275, also referred to as the n-value is ascertained on flat metal specimens such as sheets or strips. The n-value can be calculated from the raw data (force and extension) of the tensile test (e.g to EN 10002-1, ISO 6892, ASTM E8) with direct strain measurement.
Calculation to ISO 10275 Evaluation Examples Test equipment Downloads
Calculation of the n-value to ISO 10275
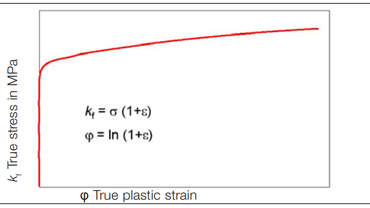
Starting point for the flow curve (Fig. “Flow curve”) with true stress kf = F/Strue where F is the current force and Strue is the true cross-section.
In particular, the determination of Strue requires precise measurement of the specimen width and specimen thickness or specimen diameter during the test. Since continuous thickness measurement during the test is not possible with sufficient accuracy, the method of volume constancy (Formula 1) (Fig. “Basis of volume constancy”) is used to calculate the true cross-section Strue. It should be noted, however, that Formula 1 can only be used up to the beginning of the local necking (generally up to Ag for RT tests). Formula 2 results from Formula 1 and is used to calculate the true cross-section. The true stress kf is thus calculated according to Formula 3 (y-axis). With the true strain φ from Formula 4 (x-axis), we then obtain the flow curve (Fig. “Flow curve”).
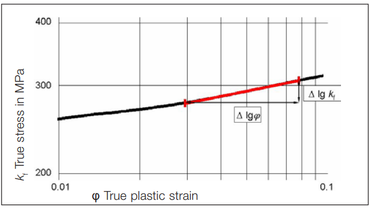
The slope of the flow curve in the double-logarithmic coordinate system (Fig. “Flow curve (double-logarithmic coordinate system)") corresponds to the hardening exponent (n-value).
Evaluation of the n-value
During the evaluation, the stress and strain values are converted into the true stress kf and true strain φ (also referred to as logarithmic deformation) via regression analysis and plotted in the double-logarithmic coordinate system. According to the least squares principle, a regression line is placed through the calculated curve points. The slope of this curve then provides the n-value. The steeper this curve rises, the more the material hardens under deformation. In general, an n-value greater than 0.22 indicates satisfactory stretch formability.
Examples of n-values of various materials
| Steel | n-value |
| Deep drawing steel DC04 | ~0.22 |
| IF steel DC06 | ~0.24 |
| Isotropic steel H250G1 | ~0.19 |
| TRIP steel TRIP700 | ~0.25 |
| Dual-phase steel H300X | ~0.15 |
| Stainless steel X5CrNi18-10 | ~0.37 |
| Aluminum AlMg5Mn (soft) | ~0.32 |
| Aluminum AlSi1,2Mg0,4 (T4) | ~0.36 |
| Copper Cu | 0.3 - 0.4 |
| Bronze CuSn | 0.3-0.6 |
| Brass CuZn37 soft | ~0.44 |